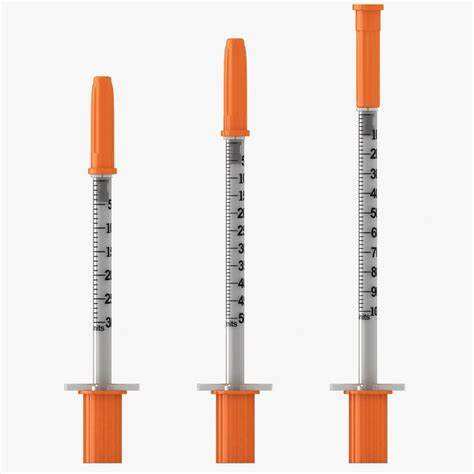
The performance of an insulin syringe is significantly influenced by needle size, a critical factor that affects both injection comfort and medication delivery accuracy. Healthcare professionals and patients must understand how needle gauge, length, and design characteristics impact the overall effectiveness of insulin administration. Proper insulin syringe selection ensures optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing patient discomfort and potential complications.
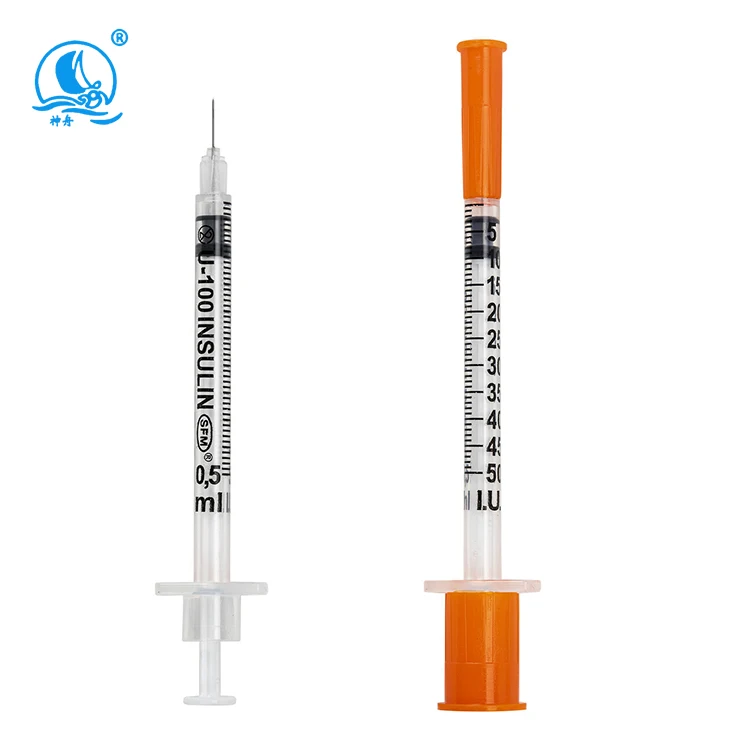
Modern insulin delivery systems have evolved considerably, with needle technology playing a pivotal role in enhancing patient compliance and treatment success. The relationship between needle specifications and injection performance encompasses multiple variables, including flow rate, injection force, tissue penetration, and patient comfort levels. Understanding these interconnected factors enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions when selecting appropriate insulin delivery devices for diverse patient populations.
Needle Gauge Impact on Injection Performance
Flow Rate Characteristics
The gauge of an insulin syringe needle directly influences the flow rate of medication delivery, with larger gauge numbers indicating smaller needle diameters. Higher gauge needles, such as 30G or 31G, create increased resistance to fluid flow, requiring greater injection pressure but offering enhanced patient comfort. Conversely, lower gauge needles facilitate faster medication delivery but may cause increased tissue trauma and patient discomfort during injection.
Clinical studies demonstrate that needle gauge selection must balance injection efficiency with patient tolerance. Ultra-fine needles reduce injection pain but extend the time required for complete medication delivery, particularly important for patients requiring larger insulin volumes. Healthcare providers must consider individual patient factors, including injection site characteristics and medication viscosity, when determining optimal needle gauge specifications.
Pressure Requirements
Injection pressure requirements vary significantly based on needle gauge selection, directly impacting the ease of insulin administration. Fine-gauge needles demand higher injection forces, potentially challenging for patients with limited hand strength or dexterity issues. This relationship between needle size and injection pressure becomes particularly relevant for elderly patients or those with arthritis who may struggle with high-resistance insulin syringes.
Modern insulin syringe designs incorporate engineering solutions to minimize injection pressure while maintaining needle fineness. Advanced needle manufacturing techniques, including specialized tip geometry and internal coating technologies, help reduce flow resistance without compromising needle strength or patient safety. These innovations enable the use of finer needles while preserving ease of injection for diverse patient populations.
Needle Length Considerations
Subcutaneous Delivery Optimization
Needle length plays a crucial role in ensuring proper subcutaneous insulin delivery while avoiding intramuscular injection complications. Standard insulin syringe needle lengths range from 4mm to 12.7mm, with shorter needles generally preferred for most adult patients. Proper needle length selection prevents inadvertent intramuscular injection, which can cause rapid insulin absorption and potentially dangerous hypoglycemic episodes.
Patient body composition significantly influences optimal needle length selection, with factors including subcutaneous tissue thickness and injection site characteristics affecting delivery accuracy. Shorter needles reduce the risk of intramuscular penetration in lean patients, while ensuring adequate subcutaneous penetration in patients with varying tissue depths. Healthcare providers must assess individual patient anatomy when recommending appropriate insulin syringe specifications.
Injection Angle Factors
Needle length directly impacts the required injection angle for optimal subcutaneous delivery, with shorter needles typically allowing for perpendicular injection techniques. Longer needles may require angled injection approaches to avoid muscle penetration, particularly in patients with limited subcutaneous tissue. This relationship between needle length and injection technique affects both delivery accuracy and patient training requirements.
Training programs for insulin syringe users must address the correlation between needle specifications and proper injection techniques. Patients using different needle lengths require specific instruction regarding appropriate injection angles, skin pinching techniques, and injection site rotation protocols. Standardizing needle length across patient populations can simplify training protocols while ensuring consistent delivery performance.
Patient Comfort and Compliance Factors
Pain Reduction Strategies
Needle size significantly impacts injection pain levels, directly affecting patient compliance with insulin therapy regimens. Ultra-fine insulin syringe needles substantially reduce injection discomfort, encouraging better adherence to prescribed treatment schedules. Studies consistently demonstrate that patients experience less injection anxiety and improved quality of life when using finer needle gauges for insulin administration.
The psychological impact of needle size on patient acceptance cannot be understated, particularly for newly diagnosed diabetic patients initiating insulin therapy. Smaller, less intimidating needles help overcome injection phobia and promote positive attitudes toward self-administration techniques. Healthcare providers should prioritize patient comfort when selecting insulin syringe specifications, as improved compliance directly correlates with better glycemic control outcomes.
Long-term Adherence Benefits
Optimal needle size selection contributes to sustained patient adherence over extended treatment periods, reducing the likelihood of therapy discontinuation due to injection-related discomfort. Patients using appropriately sized insulin syringe needles report higher satisfaction levels and demonstrate better long-term compliance with prescribed insulin regimens. This relationship between needle comfort and adherence has significant implications for diabetes management success.
Healthcare systems benefit from improved patient compliance through reduced complications and better glycemic control outcomes. Investment in high-quality insulin syringe technology with optimized needle specifications results in decreased healthcare utilization and improved patient quality of life measures. Cost-effectiveness analyses consistently support the use of patient-friendly needle designs as a valuable investment in diabetes care optimization.
Technical Manufacturing Considerations
Precision Engineering Requirements
Manufacturing precision directly impacts insulin syringe needle performance, with tight tolerances required for consistent flow characteristics and patient comfort. Advanced production techniques ensure uniform needle geometry, eliminating variations that could affect injection pressure or medication delivery accuracy. Quality control protocols must verify needle sharpness, straightness, and dimensional consistency across production batches.
Modern insulin syringe manufacturing incorporates specialized materials and coating technologies to enhance needle performance characteristics. Silicon coating applications reduce injection friction while maintaining needle integrity throughout the injection process. These technological advances enable the production of ultra-fine needles that maintain structural strength while delivering superior patient comfort and injection performance.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Comprehensive testing protocols ensure insulin syringe needle performance meets stringent medical device standards and regulatory requirements. Flow rate testing, sharpness evaluation, and strength assessment procedures verify that needle specifications deliver consistent performance across diverse clinical applications. Quality assurance programs must address both individual needle performance and batch-to-batch consistency requirements.
Regulatory compliance for insulin syringe manufacturing encompasses multiple performance criteria, including biocompatibility, sterility maintenance, and functional reliability standards. Testing protocols must demonstrate that needle size variations do not compromise safety or efficacy requirements across intended user populations. Continuous monitoring and improvement processes ensure that manufacturing capabilities keep pace with evolving clinical needs and patient expectations.
Clinical Application Guidelines
Patient Assessment Protocols
Effective insulin syringe selection requires systematic patient assessment protocols that consider individual anatomical, physiological, and lifestyle factors. Healthcare providers must evaluate subcutaneous tissue characteristics, injection site preferences, and patient dexterity levels when recommending optimal needle specifications. Standardized assessment tools help ensure consistent and appropriate insulin syringe selection across clinical settings.
Patient education programs must address the relationship between needle specifications and injection performance, enabling informed decision-making regarding insulin delivery options. Educational materials should explain how needle size affects comfort, delivery accuracy, and injection technique requirements. Comprehensive patient understanding promotes better compliance and reduces the likelihood of injection-related complications or suboptimal therapeutic outcomes.
Healthcare Provider Training
Healthcare professionals require specialized training regarding insulin syringe needle selection criteria and performance characteristics. Educational programs must address the technical aspects of needle design, flow dynamics, and patient comfort considerations. Proper training ensures that providers can make evidence-based recommendations tailored to individual patient needs and clinical circumstances.
Continuing education initiatives should keep healthcare providers informed about advancing needle technology and emerging clinical evidence regarding optimal insulin syringe specifications. Regular updates on manufacturing innovations, patient outcome data, and best practice guidelines enable providers to deliver state-of-the-art diabetes care. Interdisciplinary training programs promote consistent approaches to insulin syringe selection across healthcare team members.
Future Developments in Needle Technology
Innovation Trends
Emerging technologies promise significant advances in insulin syringe needle design and performance characteristics. Micro-manufacturing techniques enable the production of even finer needles while maintaining structural integrity and injection performance. Smart needle technologies incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to optimize injection parameters and enhance patient safety protocols.
Nanotechnology applications offer potential breakthroughs in needle surface treatments and material properties, promising enhanced comfort and performance characteristics. Research initiatives focus on developing needles with variable stiffness properties, ultra-smooth surfaces, and integrated medication delivery enhancements. These innovations aim to further reduce injection discomfort while improving delivery accuracy and consistency.
Integration with Digital Health
Future insulin syringe designs may incorporate digital connectivity features that monitor injection parameters and provide real-time feedback to patients and healthcare providers. Smart needle technology could track injection depth, flow rate, and delivery completion, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes. Integration with mobile health platforms would enable comprehensive diabetes management through enhanced injection monitoring and compliance tracking.
Artificial intelligence applications could optimize insulin syringe needle selection based on individual patient data, injection history, and physiological characteristics. Personalized needle recommendations would consider factors including tissue characteristics, injection site rotation patterns, and patient comfort preferences. These technological advances promise to revolutionize insulin delivery while maintaining the fundamental importance of appropriate needle size selection.
FAQ
What is the optimal needle gauge for most insulin syringe users
Most patients benefit from using 30G or 31G needles, which provide an excellent balance between injection comfort and medication delivery efficiency. These ultra-fine gauges significantly reduce injection pain while maintaining adequate flow rates for standard insulin volumes. Healthcare providers should assess individual patient factors, including injection site characteristics and insulin viscosity, when making specific recommendations for optimal needle gauge selection.
How does needle length affect insulin absorption rates
Needle length primarily affects injection depth rather than absorption rates, with proper subcutaneous delivery being the key factor for consistent insulin absorption. Shorter needles reduce the risk of intramuscular injection, which can cause rapid absorption and hypoglycemic episodes. Most adult patients achieve optimal results with needle lengths between 4mm and 8mm, ensuring reliable subcutaneous delivery without muscle penetration risks.
Can using the wrong needle size compromise diabetes management
Inappropriate needle size selection can significantly impact diabetes management through reduced patient compliance, injection site complications, and suboptimal medication delivery. Needles that are too large may cause excessive discomfort, leading to missed injections or poor adherence to prescribed regimens. Conversely, inadequately sized needles may result in incomplete medication delivery or improper injection depth, affecting glycemic control outcomes.
What factors should patients consider when selecting insulin syringe needle specifications
Patients should consider their subcutaneous tissue thickness, injection site preferences, hand strength, and comfort tolerance when selecting insulin syringe needle specifications. Body composition affects optimal needle length selection, while personal comfort preferences influence gauge choices. Healthcare providers should guide patients through systematic assessment protocols to identify the most appropriate needle specifications for individual circumstances and treatment requirements.