Selecting the appropriate insulin syringe is a critical decision that directly impacts diabetes management effectiveness and patient safety. Healthcare professionals and patients must carefully evaluate multiple factors to ensure optimal insulin delivery and minimize potential complications. The right insulin syringe choice can significantly improve treatment outcomes while reducing the risk of dosing errors and injection site complications that commonly affect diabetes patients worldwide.
Modern diabetes care requires precision in every aspect of treatment, and insulin delivery systems form the foundation of effective glucose control. Understanding the technical specifications, safety features, and compatibility requirements helps healthcare providers make informed decisions that benefit patient outcomes. This comprehensive evaluation process ensures that each insulin syringe selection aligns with specific treatment protocols and individual patient needs.
Essential Technical Specifications for Insulin Syringes
Volume Capacity and Measurement Accuracy
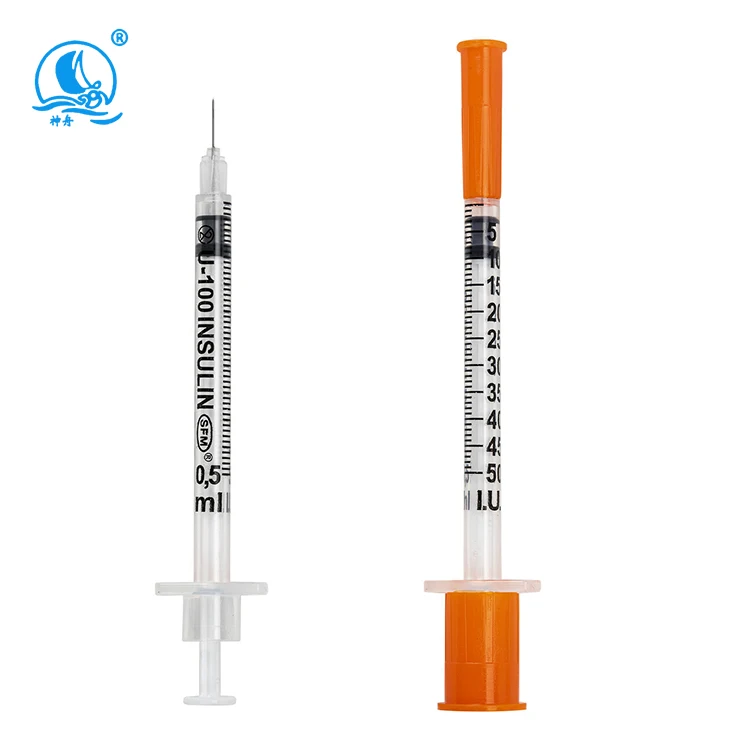
The volume capacity of an insulin syringe represents one of the most fundamental specifications that healthcare providers must evaluate. Standard insulin syringe volumes typically range from 0.3ml to 1ml, with each size designed to accommodate different insulin dosing requirements. Healthcare facilities must assess their patient population's typical insulin doses to determine the most appropriate volume range for their inventory.
Measurement accuracy becomes particularly critical when dealing with pediatric patients or adults requiring precise micro-dosing. High-quality insulin syringes feature clear, easy-to-read graduation marks that minimize dosing errors during preparation and administration. The precision of these measurements directly correlates with treatment effectiveness and patient safety outcomes in clinical settings.
Manufacturing tolerances for insulin syringe volume accuracy must meet stringent international standards, typically requiring deviation levels below 2% for optimal performance. Healthcare providers should verify that their selected insulin syringe meets or exceeds these accuracy requirements to ensure consistent medication delivery across all patient interactions.
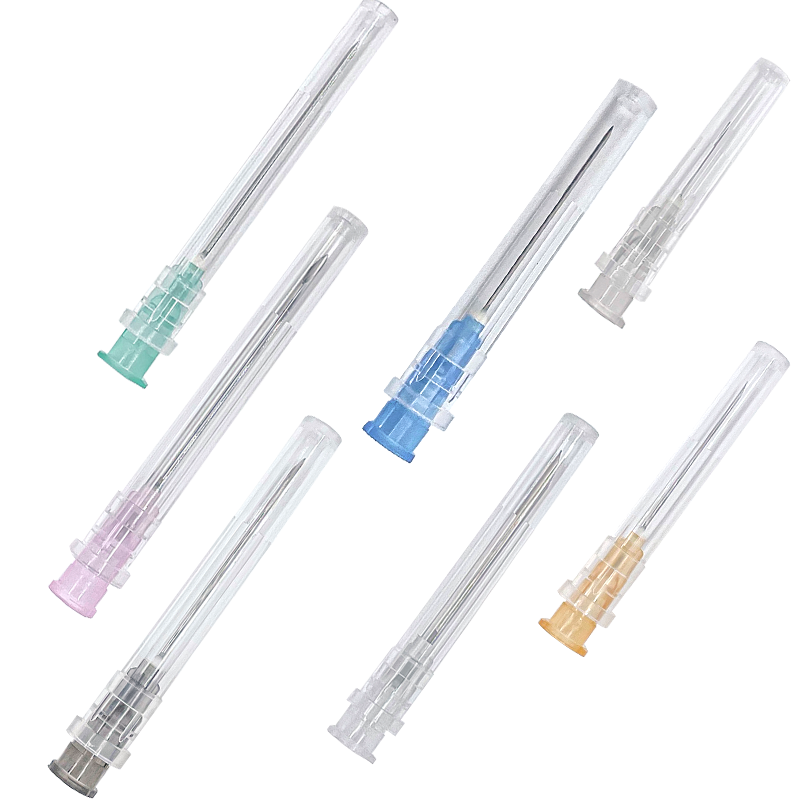
Needle Gauge and Length Considerations
Needle gauge selection significantly impacts patient comfort and insulin absorption rates during subcutaneous injections. Common insulin syringe configurations include 28-gauge, 29-gauge, and 30-gauge needles, with higher gauge numbers indicating thinner needles that typically provide enhanced patient comfort during injection procedures.
The needle length specification must align with patient body mass index and injection site characteristics to ensure proper subcutaneous delivery. Standard lengths range from 8mm to 12.7mm, with shorter needles generally preferred for pediatric applications and patients with lower body fat percentages. Healthcare providers must evaluate their patient demographics to select appropriate needle length distributions.
Advanced insulin syringe designs incorporate ultra-thin needle technology that reduces injection force requirements while maintaining structural integrity during use. These technological improvements enhance patient compliance and reduce injection-related anxiety, particularly important factors in long-term diabetes management protocols.
Safety Features and Contamination Prevention
Sterility Assurance and Packaging Integrity
Sterility assurance represents a non-negotiable requirement for any insulin syringe used in clinical or home care settings. Healthcare providers must verify that their selected products undergo appropriate sterilization processes, typically gamma radiation or ethylene oxide treatment, with documented sterility assurance levels meeting international pharmaceutical standards.
Packaging integrity directly correlates with sterility maintenance throughout the product lifecycle, from manufacturing to end-user application. Quality insulin syringe manufacturers employ multi-layer protective packaging systems that prevent contamination during storage and transportation while maintaining easy access for healthcare providers during use.
Individual insulin syringe packaging should feature tamper-evident seals and clear expiration date labeling to support proper inventory management and quality control procedures. Healthcare facilities must establish protocols for inspecting package integrity before use to maintain the highest safety standards in their diabetes care programs.
Needle Safety and Disposal Considerations
Modern insulin syringe designs increasingly incorporate safety features that minimize needlestick injury risks for healthcare providers and patients. Retractable needle mechanisms and safety caps provide additional protection during disposal procedures, reducing workplace injury incidents and improving overall safety compliance in healthcare environments.
The insulin syringe disposal process requires careful consideration of local regulations and environmental impact factors. Healthcare facilities must evaluate whether their selected products support proper sharps disposal protocols and integrate effectively with existing waste management systems to maintain regulatory compliance.
Some advanced insulin syringe models feature permanent needle attachment designs that prevent needle reuse and reduce cross-contamination risks. These safety enhancements become particularly valuable in high-volume clinical settings where multiple healthcare providers handle diabetes care responsibilities.
Compatibility and Integration Requirements
Insulin Type and Concentration Compatibility
Different insulin formulations require specific handling considerations that influence insulin syringe selection criteria. Rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting insulin types may have varying viscosity characteristics that affect injection performance and patient comfort levels during administration procedures.
Insulin concentration specifications, particularly the distinction between U-100 and U-500 formulations, mandate corresponding insulin syringe designs with appropriate measurement scales. Healthcare providers must ensure their selected syringes match the insulin concentration being administered to prevent dangerous dosing errors that could result in hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes.
Some insulin formulations contain suspended particles that require gentle mixing before administration, necessitating insulin syringe designs that accommodate this preparation process without compromising measurement accuracy or sterility. Healthcare providers should verify compatibility between their insulin inventory and proposed syringe specifications before making procurement decisions.
Healthcare System Integration
Healthcare system integration extends beyond individual product performance to encompass supply chain management, staff training requirements, and quality assurance protocols. Insulin syringe standardization across departments can reduce training complexity and minimize medication errors while supporting efficient inventory management processes.
Electronic health record systems may require specific insulin syringe product codes and specifications for accurate documentation and billing procedures. Healthcare providers should evaluate whether their selected products integrate seamlessly with existing information management systems to support comprehensive patient care documentation.
Cost-effectiveness analysis should consider not only initial insulin syringe procurement costs but also associated training expenses, disposal fees, and potential liability implications. Long-term healthcare system sustainability requires balanced consideration of quality, safety, and economic factors in product selection decisions.
Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturing Standards and Certification
Quality insulin syringe manufacturers maintain rigorous quality control systems that encompass raw material sourcing, production processes, and final product testing procedures. Healthcare providers should verify that their selected suppliers hold appropriate regulatory certifications, including FDA approval for United States markets and CE marking for European distribution.
International Organization for Standardization compliance, particularly ISO 13485 for medical device quality management systems, provides additional assurance of consistent manufacturing practices and quality control procedures. These certifications demonstrate manufacturer commitment to maintaining high-quality standards throughout their insulin syringe production processes.
Batch testing documentation and certificate of analysis availability support healthcare facility quality assurance programs and regulatory compliance requirements. Healthcare providers should establish relationships with insulin syringe suppliers who provide comprehensive testing documentation and maintain transparent quality control procedures.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Healthcare facilities must maintain detailed documentation regarding insulin syringe procurement, usage, and disposal procedures to support regulatory compliance and quality improvement initiatives. Proper documentation systems enable effective lot tracking and recall procedures if quality issues arise with specific product batches.
Regulatory compliance extends to staff training documentation and competency verification for insulin syringe handling procedures. Healthcare providers should establish comprehensive training programs that address proper selection, preparation, administration, and disposal techniques to maintain consistent care quality across all patient interactions.
Risk management protocols should address potential complications associated with insulin syringe use, including dosing errors, injection site reactions, and device malfunction scenarios. Proactive risk assessment and mitigation strategies support patient safety while protecting healthcare organizations from potential liability issues.
Patient-Specific Selection Criteria
Individual Patient Characteristics
Patient age, cognitive function, and manual dexterity significantly influence appropriate insulin syringe selection for home care applications. Pediatric patients may require specialized insulin syringe designs with enhanced safety features and age-appropriate measurement scales that support accurate dose preparation by caregivers.
Visual impairment considerations necessitate insulin syringe designs with high-contrast measurement markings and tactile feedback features that support accurate dose preparation. Healthcare providers should assess individual patient capabilities and limitations when recommending specific insulin syringe products for home use applications.
Injection frequency requirements influence insulin syringe selection, particularly for patients requiring multiple daily injections who may benefit from comfort-enhanced needle designs and ergonomic syringe configurations. Patient compliance improves when insulin delivery systems minimize discomfort and simplify administration procedures.
Long-term Treatment Considerations
Long-term diabetes management requires insulin syringe selections that support consistent treatment adherence and minimize injection site complications. Rotating needle gauge and length specifications may help prevent lipodystrophy and other injection site issues that commonly develop with prolonged insulin therapy.
Storage and portability requirements become important factors for patients who travel frequently or require insulin administration outside their home environment. Insulin syringe packaging and design should support safe transportation while maintaining sterility and ease of use in various settings.
Cost considerations for long-term treatment include insurance coverage limitations and out-of-pocket expenses that may influence patient compliance with prescribed insulin regimens. Healthcare providers should consider the economic impact of their insulin syringe recommendations on individual patient circumstances and treatment sustainability.
FAQ
What volume capacity should I choose for an insulin syringe
The appropriate volume capacity depends on your typical insulin doses and injection frequency. For doses under 30 units, a 0.3ml insulin syringe provides better measurement precision, while 0.5ml to 1ml capacities work well for larger doses. Healthcare providers should assess individual patient dosing requirements and recommend the smallest volume that accommodates the prescribed dose range to maximize measurement accuracy.
How do needle gauge and length affect injection comfort
Higher gauge numbers indicate thinner needles that generally provide enhanced comfort during injection, with 30-gauge needles offering the least discomfort. Needle length should be selected based on body mass index and injection site characteristics, with shorter needles typically preferred for pediatric patients and individuals with lower body fat percentages to ensure proper subcutaneous delivery.
What safety features should I prioritize in insulin syringe selection
Priority safety features include sterility assurance through appropriate packaging, needle safety mechanisms to prevent accidental sticks, and clear measurement markings to minimize dosing errors. Look for insulin syringe products with tamper-evident packaging, individual sterile wrapping, and measurement scales that match your insulin concentration to ensure safe and accurate administration.
How do I ensure compatibility between insulin types and syringe specifications
Verify that your insulin syringe measurement scale matches your insulin concentration, particularly distinguishing between U-100 and U-500 formulations to prevent dosing errors. Consider insulin viscosity characteristics and any mixing requirements when selecting needle gauge, and consult with healthcare providers to confirm that your chosen insulin syringe specifications align with your prescribed insulin type and dosing regimen.

