Managing diabetes effectively requires precise medication delivery, and the choice of injection device plays a crucial role in patient outcomes. An insulin syringe represents one of the most reliable and cost-effective methods for administering insulin therapy, offering diabetic patients greater control over their daily medication routine. Modern insulin syringes have evolved significantly from their early designs, incorporating advanced features that enhance accuracy, safety, and user convenience. The traditional insulin syringe remains a cornerstone of diabetes care, particularly for patients who require flexible dosing options or have specific medical considerations that make alternative delivery methods less suitable.
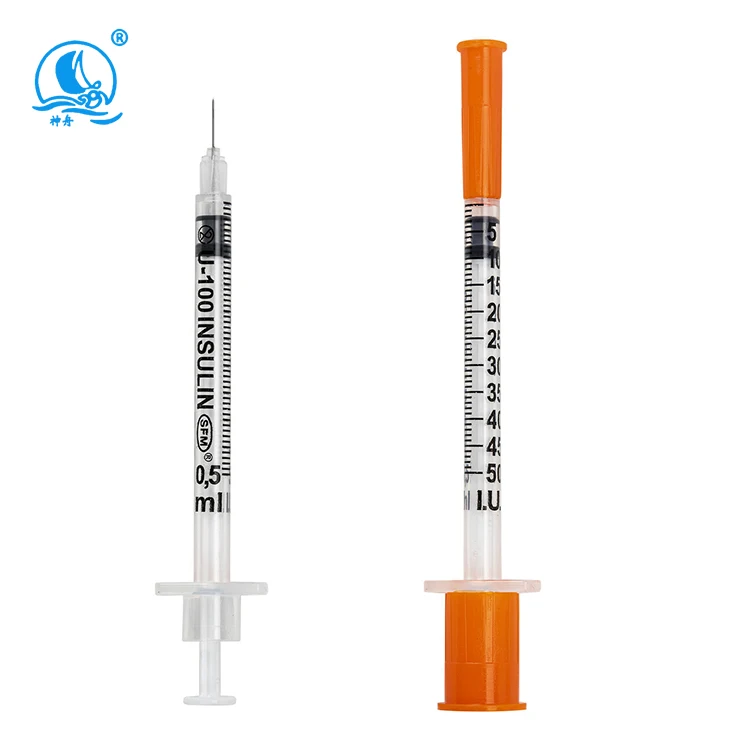
Understanding Modern Insulin Syringe Technology
Precision Engineering for Accurate Dosing
Contemporary insulin syringe design incorporates precision manufacturing techniques that ensure consistent dosing accuracy. The graduated markings on modern syringes are laser-etched or molded with exceptional precision, allowing healthcare providers and patients to measure insulin doses with remarkable accuracy. Each insulin syringe undergoes rigorous quality control testing to verify that volume measurements remain within strict tolerances, typically maintaining accuracy levels within 2-3% of the intended dose.
The barrel design of a quality insulin syringe features smooth internal surfaces that minimize insulin adhesion and ensure complete medication delivery. Advanced materials used in syringe construction reduce the likelihood of dose retention, which can occur with inferior products. This precision becomes particularly important for patients requiring small insulin doses, where even minor variations could significantly impact blood glucose control.
Needle Technology and Patient Comfort
Modern insulin syringe needles incorporate ultra-fine gauge technology that significantly reduces injection discomfort while maintaining optimal flow rates. The needle tips undergo specialized sharpening processes that create beveled edges designed to penetrate skin tissue with minimal trauma. Silicon coating on many insulin syringe needles provides additional lubrication, further enhancing patient comfort during injection procedures.
Needle length options in insulin syringe products cater to different patient populations and injection site preferences. Shorter needles reduce the risk of intramuscular injection while longer options accommodate patients with different body compositions. The integration of safety features in some insulin syringe designs helps prevent needle-stick injuries and supports proper disposal practices.
Clinical Advantages in Diabetes Management
Flexible Dosing Capabilities
The insulin syringe offers unparalleled flexibility for patients requiring customized insulin dosing regimens. Unlike pre-filled insulin pens that may limit dosing increments, an insulin syringe allows for precise adjustment of medication amounts based on individual patient needs, meal composition, blood glucose levels, and activity patterns. This flexibility proves particularly valuable for patients with varying insulin sensitivity throughout different times of the day.
Healthcare providers often prefer prescribing insulin syringe therapy for patients who require dose adjustments during illness, stress, or other physiological changes that affect insulin requirements. The ability to draw exact amounts from insulin vials provides therapeutic advantages in situations where standard pen cartridge doses may not align with optimal patient care. Complex insulin mixing protocols also benefit from the precision offered by quality insulin syringe products.
Economic Benefits and Accessibility
Cost considerations play a significant role in long-term diabetes management, and the insulin syringe typically represents the most economical injection method available to patients. The lower per-dose cost compared to insulin pens makes insulin syringe therapy accessible to broader patient populations, particularly in healthcare systems with limited resources. Insurance coverage for insulin syringe supplies often provides more comprehensive benefits than alternative delivery methods.
The widespread availability of insulin syringe products ensures consistent access to diabetes supplies across diverse geographic locations. Manufacturing scalability allows for reliable supply chains that support global diabetes care initiatives. This accessibility factor becomes crucial for maintaining consistent therapy adherence, particularly in underserved communities where specialized diabetes supplies may be limited.
Safety Features and Risk Mitigation
Contamination Prevention Protocols
Modern insulin syringe manufacturing incorporates sterile packaging and single-use design principles that minimize contamination risks during diabetes self-care procedures. Each insulin syringe undergoes sterilization processes that eliminate potential pathogens while maintaining material integrity. Sealed packaging protects sterility until the moment of use, supporting infection control practices in both clinical and home care settings.
Quality insulin syringe products feature tamper-evident packaging that provides visual confirmation of product integrity. The single-use nature of disposable insulin syringes eliminates cross-contamination risks that could occur with reusable injection devices. Proper disposal protocols for used insulin syringe units support public health initiatives and environmental safety standards.
Dosing Error Prevention
Clear graduated markings on insulin syringe barrels help prevent dosing errors that could lead to dangerous hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes. Color-coded insulin syringe options allow patients and caregivers to quickly identify different insulin concentrations, reducing the risk of medication mix-ups. Some insulin syringe designs incorporate visual enhancement features that improve readability for patients with vision impairments.
The transparent barrel design of quality insulin syringe products enables visual verification of proper medication drawing and air bubble detection. This transparency supports safe injection practices by allowing users to confirm accurate dose preparation before administration. Training programs often emphasize these visual confirmation steps as essential components of safe insulin syringe technique.
Patient Training and Technique Optimization
Proper Injection Methodology
Effective insulin syringe use requires proper injection technique training that covers site preparation, needle insertion angles, and medication administration protocols. Healthcare providers typically demonstrate optimal insulin syringe handling procedures during initial diabetes education sessions, emphasizing the importance of consistent technique for therapeutic success. Rotation of injection sites prevents lipodystrophy development and ensures consistent insulin absorption rates.
Patient education programs should address proper insulin syringe storage, handling, and disposal procedures to maximize safety and effectiveness. Temperature considerations for both insulin medications and insulin syringe storage help maintain product stability and performance. Regular technique review sessions support ongoing adherence to best practices and identify opportunities for improvement in diabetes self-care routines.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common insulin syringe usage challenges include air bubble formation, needle clogging, and dose measurement difficulties. Proper training addresses these issues through systematic approaches that ensure consistent medication delivery. Air bubble removal techniques using the insulin syringe become second nature with appropriate instruction and practice opportunities.
Patients should understand how to identify and address insulin crystallization issues that may affect syringe function. Quality insulin syringe products minimize these complications through superior materials and manufacturing processes, but patient awareness remains important for optimal outcomes. Regular healthcare provider consultation supports troubleshooting efforts and ensures continued therapeutic success.
Quality Considerations and Product Selection
Manufacturing Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Selecting quality insulin syringe products requires understanding relevant manufacturing standards and regulatory approvals that ensure patient safety and product effectiveness. International standards organizations establish guidelines for insulin syringe design, materials, and performance characteristics that reputable manufacturers must meet. Regulatory agencies conduct ongoing oversight of insulin syringe production facilities to maintain consistent quality levels.
Quality assurance protocols in insulin syringe manufacturing include testing for dimensional accuracy, sterility, needle sharpness, and material compatibility with insulin formulations. Batch testing procedures verify that each production lot meets established specifications before distribution to healthcare providers and patients. Documentation of quality control measures supports traceability and enables rapid response to any product issues.
Material Science and Biocompatibility
Advanced materials used in insulin syringe construction undergo extensive biocompatibility testing to ensure safe contact with both insulin medications and human tissue. Polymer selection affects syringe durability, insulin stability, and patient comfort during injection procedures. Surface treatments and coatings applied to insulin syringe components enhance performance while maintaining safety profiles.
Research into new materials for insulin syringe applications continues to drive improvements in product performance and patient experience. Innovations in needle metallurgy, barrel polymers, and plunger design contribute to ongoing evolution in insulin delivery technology. These advances support improved diabetes management outcomes while maintaining the cost-effectiveness that makes insulin syringe therapy accessible to diverse patient populations.
FAQ
How often should insulin syringes be replaced during treatment
Insulin syringes are designed for single-use only and should never be reused for subsequent injections. Each insulin syringe maintains optimal sterility and needle sharpness for only one injection cycle. Reusing insulin syringes increases infection risk, reduces injection comfort due to dulled needles, and may compromise dosing accuracy. Patients should dispose of used insulin syringes immediately after injection in appropriate sharps containers and use a fresh syringe for each insulin dose.
What size insulin syringe is most appropriate for different dosing needs
Insulin syringe selection depends primarily on the maximum dose required and the desired measurement precision. For doses up to 30 units, a 0.3mL insulin syringe provides the finest graduation markings and greatest accuracy. Doses between 30-50 units work well with 0.5mL insulin syringe options, while larger doses up to 100 units require 1mL insulin syringe capacity. The smaller the syringe volume relative to the dose, the more precise the measurement becomes for optimal diabetes management.
Can insulin syringes be used with all types of insulin formulations
Most insulin syringe products are compatible with standard insulin concentrations including U-100 formulations commonly prescribed for diabetes management. However, patients should verify insulin syringe compatibility with specific insulin types, particularly with newer concentrated formulations like U-200 or U-500 insulins. The graduated markings on standard insulin syringes correspond to U-100 insulin concentrations, so using different insulin strengths requires dose calculation adjustments to ensure accurate medication delivery.
How should insulin syringes be stored to maintain product quality
Proper insulin syringe storage involves keeping unopened packages in clean, dry environments at room temperature away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Insulin syringes should remain in original packaging until use to maintain sterility and protect from contamination. Avoid storing insulin syringe supplies in bathrooms or other high-humidity areas that could compromise packaging integrity. Check expiration dates regularly and rotate stock to ensure optimal product performance when needed for diabetes care.