Ymmärtäminen Ruisku Uudellekkäytön riskejä
Toistuvan neulan käytön vaarat
Miksi neulankäytön uudelleenkäyttö on niin riskialtista? Saman neulan käyttäminen uudelleen voi aiheuttaa vakavia ongelmia kaikille osapuolille. Puhumme vakavista infektioista, kuten HIV ja hepatiitti B/C, jotka voivat leviämään, kun neuloja ei steriloida asianmukaisesti käyttökertojen välillä. Jotkut tutkimukset osoittavat, että noin joka kolmannes rokotteista, jotka annetaan likaisilla neuloilla, leviättää näitä viruksia. Myös lääkärit ja heidän potilaansa kohtaavat toisenlaisen vaaran – sattuman neulatapaturmat käsittelyn yhteydessä. Näitä pieniä onnettomuuksia voi vaikuttaa vähäisiltä, mutta ne avaa oven lukuisille taudinaiheuttajille päästäkseen elimistöön. Älä myöskään unohda, mitä tapahtuu vanhoille neuloille, kun niitä käytetään uudelleen. Ne kuluvat, taipuvat, eivätkä ne välttämättä kestäkään käyttöä. Tällöin neuloinnit aiheuttavat potilaille enemmän kipua, ja vielä pahempaa on, että lääkkeet eivät toimi yhtä tehokkaasti, koska vaurioituneet neulat eivät pysty toimittamaan lääkkeitä oikein kehoon. Kivunhallinta vaikeutuu ja hoitotulokset kärsivät sen seurauksena.
Miten saastuneet hypodermiatartit levittävät tautia
Sairauksien leviämiseen vaikuttavat saastuneet ruiskut, jotka pystyvät kuljettamaan mukanaan lukuisia vaarallisia mikrobeja. Tutkimukset osoittavat, että kyseessä on merkittävä ongelma, sillä joissakin tutkimuksissa arvioidaan, että turvattomien ruiskujen osuus tällä tavoin leviävissä infektioissa saattaa olla jopa noin 60 prosenttia. Pääongelma syntyy, kun lääkärit ja muu terveydenhuollon henkilökunta käyttää neuloja uudelleen ilman niiden asianmukaista puhdistusta. Tämä luo suoran tien verensiirron kautta leviäville sairauksille siirtyä henkilöltä toiselle, mikä selittää, miksi sairaaloissa voi joskus esiintyä yllättäviä sairaskausiin liittyviä puhkeamisia. Asiaa pahentaa vielä se, että tiettyjen bakteerien, kuten MRSA:n ja Clostridium difficile -bakteerin, tiedetään selviytyvän hyvin käytetyistä neuloista, joita ei ole hävitetty tai kierrätetty oikein. Kun terveydenhuollon ammattilaiset ymmärtävät tilanteen vakavuuden, heidän käyttäytymisensä muuttuu usein tiukemmiksi ruiskujen käsittelyohjeiksi, mikä on ymmärrettävää, kun otetaan huomioon seuraukset, joita muuten voi syntyä.
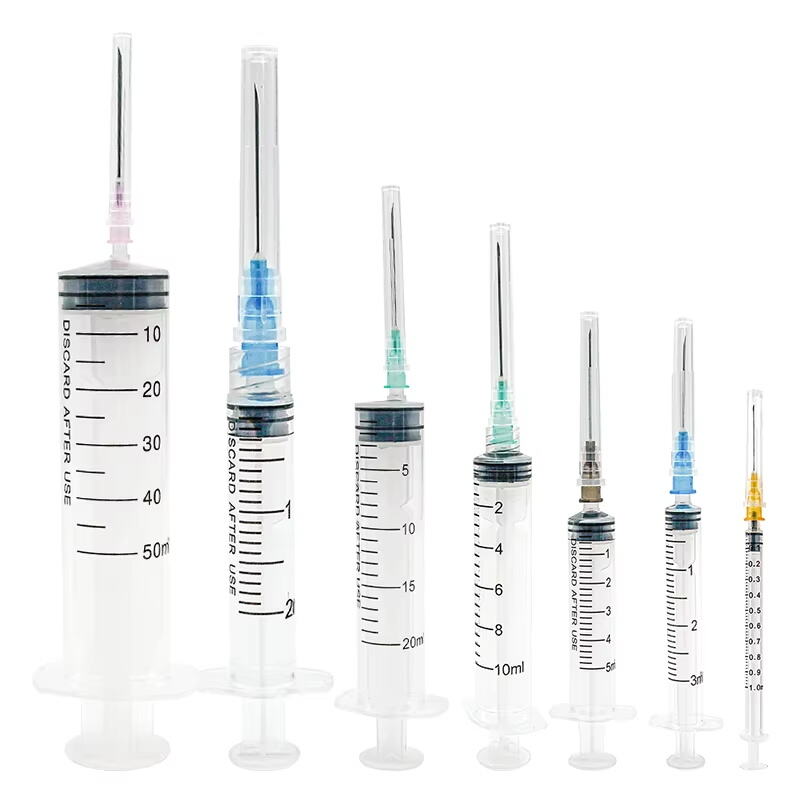
Perustiedot lääketieteellisten tarttien keskeisistä komponenteista
3ml- ja 10ml-tarttien rakenteellinen vertailu
Mikä todella erottaa 3 ml:n ja 10 ml:n kynätysruiskut toisistaan? Ruiskujen toiminnan ymmärtäminen on erittäin tärkeää valittaessa oikea ruisku tiettyyn tehtävään, erityisesti kun vertaa näitä kahta kokoa rinnakkain. 3 ml:n versio soveltuu yleensä pieniin määriin, kuten lapsille tai tilanteisiin, joissa lääkemäärän täytyy olla tarkasti oikea. Sen sijaan 10 ml:n ruiskua käytetään yleisesti suurempien annosten yhteydessä, jotka ovat tavallisia aikuisten hoidossa tai aina kun lääkemäärä on huomattavan suuri. Näiden ruiskujen ero ei koske pelkästään kokoa. Myös liipäisijät vaihtelevat, mukavuuspinnat ovat eri pituisia, eikä myöskään niiden kärjet ole täysin samanlaisia. Kaikki nämä yksityiskohdat ovat tärkeitä lääkkeiden tarkan annostelun kannalta, mikä on terveydenhuollon ammattilaisille tuttua tietoa vuosien kokemuksen kautta. Näiden erojen tuntemus vähentää myös virheiden mahdollisuutta neulottamisessa, mikä lisää kaikkien osapuolten turvallisuuden tunnetta.
Ilman neulaa suunniteltujen tarkoituksena
Neeserittömät ruiskut tuovat todellisia etuja nykylääketieteeseen, erityisesti kun on hoidettava suuria määriä potilaita yhtä aikaa. Ne vähentävät pelättyjä neulastuksia, joihin monet sairaanhoidon työntekijät kohtaavat päivittäin. Potilaille, joille neulat aiheuttavat ahdistusta, tämä suunnittelu tekee suuren eron hoidon aikana kokeitavassa mukavuudessa. Toisena merkittävänä etuna on infektioiden leviämisen riskin väheneminen potilaiden välillä, koska mukana ei ole jaettuja laitteita. Klinikoissa, jotka käyttävät näitä laitteita, on myös raportoitu parantunutta rokotusaikataulujen noudattamista. Kun satojen tai jopa tuhansien ihmisten on saatava rokotuksia nopeasti, kuten tautiputkien tai tavallisen influenssakauden aikana, neeserittömät järjestelmät tekevät koko prosessista nopeamman ja turvallisemman. Eri erikoisalojen terveydenhuollon palveluntarjoajat käyttävät yhä enemmän näitä teknologioita, koska ne toimivat käytännössä selvästi paremmin kuin perinteiset menetelmät.
Turvalliset valmistelu- ja käsittelymenetelmät
Steriliointiteknikat uudelleenkäytettäville osille
Mitä sitten pidetään hyvinä sterilointimenetelminä? No, suurin osa lääkintälaitoksista käyttää menetelmiä, kuten höyrysterilointia tai etyleenioksidikäsittelyä, joilla varmistetaan toistuvasti käytettävien ruiskujen osien turvallisuus. Näillä menetelmillä tappaa käytännössä kaikki mikrobit ja bakteerit, jotka muuten voisivat päätyä jonkun verenkiertoon. Centers for Disease Control -keskuksen mukaan heidän yksityiskohtaisia sterilointiohjeitaan noudattaminen ei ole vain suositeltavaa, vaan käytännössä pakollista, jos sairaaloiden halutaan vältettävän tartuntojen leviämistä potilaiden välillä. Kun henkilökunta jättää vaiheita tekemättä tai kiirehtii prosessin läpi, tapahtuu vakavia virheitä – olemme nähneet kokonaisia osastoja suljettuna aiemmin saastuneen laitteen vuoksi. Siksi jatkuvat koulutusjaksot ovat niin tärkeitä, koska ne auttavat sairaanhoitajia ja teknikoita muistamaan tarkasti, miten jokaista osaa tulee käsitellä oikein ja ilman sääntöjen vähättelyä. Parempi sterilointi tarkoittaa vähemmän sairaalainfektioita, mikä lopulta pelastaa ihmishenkiä ja estää terveydenhuoltokustannusten karkaamista hallinnasta.
Oikeat lääkemuotojen mittaamisen ohjeet
Lääkemäärin oikea mittaaminen on erittäin tärkeää. Kun lääkkeitä ei mitata oikein, potilailla on riski saada liikaa tai liian vähän lääkettä, mikä voi olla vaarallista etenkin sairaaloiden tehohoito-osastoilla. Hoitajien ja lääkäreiden täytyy valita jokaisessa tilanteessa oikeanlainen ruisku, koska eri koot ovat tärkeitä annettaessa tiettyjä annoksia. Useimmat terveydenhuollon ammattilaiset noudattavat tiukkoja protokollia tässä asiassa ja tarkistavat sekä tarkistavat uudelleen luvut ennen kuin antavat potilaalle lääkkeen. Ajattele sitä näin: kuvittele, että lääkäri antaa puolet siitä mitä tarvitaan infektiota hoidettaessa vain siksi, että sattumalta valittiin väärän kokoinen neula. Siksi sairaaloissa on suuria mainoksia lääkityskärryjen vieressä, joiden tehtävänä on muistuttaa henkilökuntaa käyttämään riittävästi aikaa laskemiseen. Näiden yksityiskohtien oikeellisuudella varmistetaan, että hoidot toimivat tarkoitetulla tavalla ja että kaikkien turvallisuus säilyy prosessin aikana.
Lisätietoja tarkasta annostelusta saat syrjyn mittausturvallisuutta koskevista ohjeista.
Askareiden antamisen parhaat käytännöt vaiheittain
Ihon valmistelu ja neulan asetuskulmat
Kun on kyse ruiskuttamisesta, on useita asioita, joilla on todellista merkitystä. Ensinnäkin ihon oikea valmistelu ja neulan oikea kulma vaikuttavat suuresti. Alueen puhdistaminen antiseptisesti ennen neulan asettamista vähentää infektioiden riskiä huomattavasti. Tutkimukset osoittavat, että oikea puhdistus voi vähentää infektioprosenttia jopa noin 10 prosentista alle 1 prosentin. Tällainen huolellisuus varmistaa lääkkeen toimivan oikeassa kohdassa aiheuttamatta lisäongelmia myöhemmin. Neulan kulma vaihtelee riippuen siitä, minkälaisesta ruiskutuksesta on kyse. Lihasruiskutuksessa neula suunnataan suoraan 90 asteen kulmassa, kun taas rasvakudosruiskutuksessa tarvitaan noin 45 asteen kulma. Oikean kulman käyttö estää tarpeetonta kipua ja kudosvaurioita. Lääkärien ja hoitajien tulisi päivittää taitojaan säännöllisesti näissä perusasioissa, koska potilaat huomaavat, kun toimenpiteet tehdään huolellisesti eikä niitä vain kiirehditä. Hyvä teknikka johtaa parempiin tuloksiin ja iloisempiin potilaisiin yhteensä.
Ilmapuun ja kudosvahingon ehkäisy
Mikä on paras tapa päästä eroon ilmakuplista, kun annetaan ruisketuksia? Ilmakupolien poistaminen ja samalla kudosvaurioiden estäminen ruiskutuksien yhteydessä on erittäin tärkeää oikean annosmäärän saavuttamiseksi ja potilaiden turvallisuuden varmistamiseksi. Kun ruiskussa on ilmakuplia, ihmiset eivät joskus saa tarpeeksi lääkettä, mikä tekee hoitojen tehokkuudesta heikomman. Siksi sairaanhoitajien ja lääkäreiden tulisi tietää, kuinka ilmakuplat poistetaan oikein. Ruiskujen oikea käsittely ja neulan oikea asettaminen auttavat estämään myöhemmin mahdollisesti esiintyviä kudosvaurioita, kuten absessien muodostumista. Terveydenhuollon henkilökunnan tulisi todella keskittyä hyviin tekniikoihin ilmakupolien poistamiseksi ja oikean pistospotin valitsemiseen. Riittävän koulutuksen ja parhaiden käytäntöjen noudattamisen avulla lääkärit voivat välttää tarpeettomia kudosvaurioita ja varmistaa, että hoidot toimivat potilailla tarkoitetulla tavalla.
Käytettyjen ruiskojen hävittämisen protokollat
Biologisen vaaran säiliöiden vaatimukset
Biologisen vaaran roskakuljetuksen vaatimukset ovat erittäin tärkeitä, kun kyseessä on käytettyjen neulojen turvallinen hävittäminen ja kaikkien, sekä yleisön että sairaanhoidon henkilökunnan, turvallisuuden takaaminen. Säiliöiden täytyy noudattaa OSHA:n ja CDC:n sääntöjen mukaisia tiukkoja sääntöjä. Niiden tulee olla läpäisynkestoisia, täysin vuotoonkestäviä ja visuaalisesti erottuvia, jotta ihmiset tietävät, mitä niissä on. Näin tiukat standardit on asetettu, jotta varmistetaan, että kukaan ei loukkaudu käsitellessään tai törmätessään hylättyihin ruiskuihin. Säännölliset roskien hävitysaikataulut ja selkeät hävitysohjeet auttavat pitämään säiliöt vähän täynnä ja estämään onnettomuuksia, joissa joku saattaa koskea vaaralliseen esineeseen. Kun sairaalat ja klinikat noudattavat näitä turvallisuustoimia, ne tarjoavat parempaa suojaa ei vain työntekijöilleen, vaan myös kaikille paikalle tuleville.
Yhteisöjen ruisku-ohjelmat
Mikä tekee yhteisöjen neulank palautusohjelmista niin tehokkaita turvallisuuden kannalta? No, nämä ohjelmat vähentävät käytettyjen neulojen määrää, jotka lojuvat puistoissa, sivukatuilla ja muilla julkisilla alueilla, joihin ihmiset voivat vahingossa astua. Tämä tarkoittaa sitä, että ohimeneviltä jalkapyykiltä aiheutuvat neulankolaskelmat vähenevät. Antamalla ihmisille turvallisen tavan hävittää neuloja, monet ohjelmat opettavat myös paikallisille, mitä tapahtuu, jos neuloja hävitetään väärin. Joidenkin kaupunkien ongelmat ovat vähenneet merkittävästi näiden keräyspisteiden perustamisen jälkeen. Otetaan esimerkiksi Chicago, jossa ilmoitettiin yli 50 % vähemmän käytettyjen neulojen aiheuttamia tapahtumia, kun ohjelma oli käynnissä. Kun tavalliset ihmiset tietävät, minne he voivat viedä käytetyt välineensä, heistä tulee osa ratkaisua eikä ongelmaa. Asianmukaisten hävitysvaihtoehtojen saanti tekee todella kaupunginosista turvallisempia kokonaisuudessaan ja samalla suojellaan kansanterveyttä.
UKK
Miksi neuloiden uudelleenkäyttö on vaarallista?
Ruiskujen uudelleenkäyttö aiheuttaa merkittäviä terveysriskejä, kuten HIV- ja hepatiitti B/C-tartunnat, ja heikentää neulaa, mikä johtaa lisääntyneeseen kipuun ja tehottomaan lääkkeen toimitukseen.
Miten saastuneet hypodermiapistollit levittävät tautia?
Saastuneet hypodermiapistollit voivat levittää patogeenia ja verensairauksia nopeasti, erityisesti kun niitä käytetään uudelleen ilman asianmukaista sterilointia, mikä johtaa korkeisiin levitysvaaroihin.
Mitkä ovat tehokkaita sterilointitekniikoita?
Tekniikat, kuten autoklaavi ja etyylioksidihoito, ovat olennaisia poistaa patogeenit uudelleenkäytettävistä hypodermiapistolin osista, estämällä infektioiden leviämisen.
Miten lääkkeet mitataan tarkasti?
Tarkka lääkemittaaminen vaatii oikean tyypin ja koon syringin käytön, annosten kaksoistarkastuksen sekä vahvistettujen ohjeiden noudattamisen välttääkseen ylikannoksen tai alikannoksen.
Mitkä ovat biologisten hankintojen säilöiden vaatimukset?
Biologiset hankinnat säilöt täytyy olla pistoarvoisia, vuotoomittaisia ja helposti tunnistettavissa varmistaakseen käytettyjen syringoiden turvallinen hävittäminen, noudattaen OSHA:n ja CDC:n standardeja.
Miten yhteisölliset syringepalautusohjelmat parantavat turvallisuutta?
Hypodermianpalausohjelmat tarjoavat turvallisia hylkäämisresursseja, vähentävät julkisten alueiden neulahyökkäyksiä ja nostavat tietoisuutta oikeasta hylkäämisprotokollasta, mikä lopulta parantaa yhteisön turvallisuutta.
Sisällys
- Ymmärtäminen Ruisku Uudellekkäytön riskejä
- Perustiedot lääketieteellisten tarttien keskeisistä komponenteista
- Turvalliset valmistelu- ja käsittelymenetelmät
- Askareiden antamisen parhaat käytännöt vaiheittain
- Käytettyjen ruiskojen hävittämisen protokollat
-
UKK
- Miksi neuloiden uudelleenkäyttö on vaarallista?
- Miten saastuneet hypodermiapistollit levittävät tautia?
- Mitkä ovat tehokkaita sterilointitekniikoita?
- Miten lääkkeet mitataan tarkasti?
- Mitkä ovat biologisten hankintojen säilöiden vaatimukset?
- Miten yhteisölliset syringepalautusohjelmat parantavat turvallisuutta?

