Understanding Syringe Reuse Risks
Dangers of Repeated Needle Use
What makes reusing syringes so risky? Using the same needle over and over can really mess things up for everyone involved. We're talking about serious infections here, stuff like HIV and Hepatitis B/C getting passed around when needles aren't properly sterilized between uses. Some studies show that roughly one in thirty shots given with dirty needles actually spreads these viruses. Both medical staff and their patients face another danger too - accidental needle sticks during handling. These little accidents might seem minor but they open doors for all sorts of nasty bugs to enter the body. And let's not forget what happens to those old needles after repeated use. They get worn down, bent, maybe even develop tiny cracks. When this happens, injections become much more painful for patients, and worse still, medications don't work as well because the damaged needles struggle to deliver drugs properly throughout the body. Pain management becomes harder and treatment outcomes suffer as a result.
How Contaminated Syringes Spread Disease
Contaminated syringes play a major role in spreading diseases through their ability to carry all sorts of dangerous germs. Research shows just how big a problem this really is, with some studies suggesting that unsafe syringes might be responsible for around 60 percent of infections transmitted this way. The main issue occurs when medical staff reuse needles without cleaning them properly first. This creates a fast track for bloodborne illnesses to jump from one person to another, which explains why hospitals sometimes see sudden outbreaks. Things get even worse because certain bacteria like MRSA and Clostridium difficile actually survive quite well on used needles that haven't been disposed of correctly or recycled improperly. When healthcare workers understand what's at stake here, they tend to follow stricter guidelines about handling syringes, which makes sense considering what could happen otherwise.
Essential Components of Medical Syringes
Anatomy of 3ml vs. 10ml Syringes
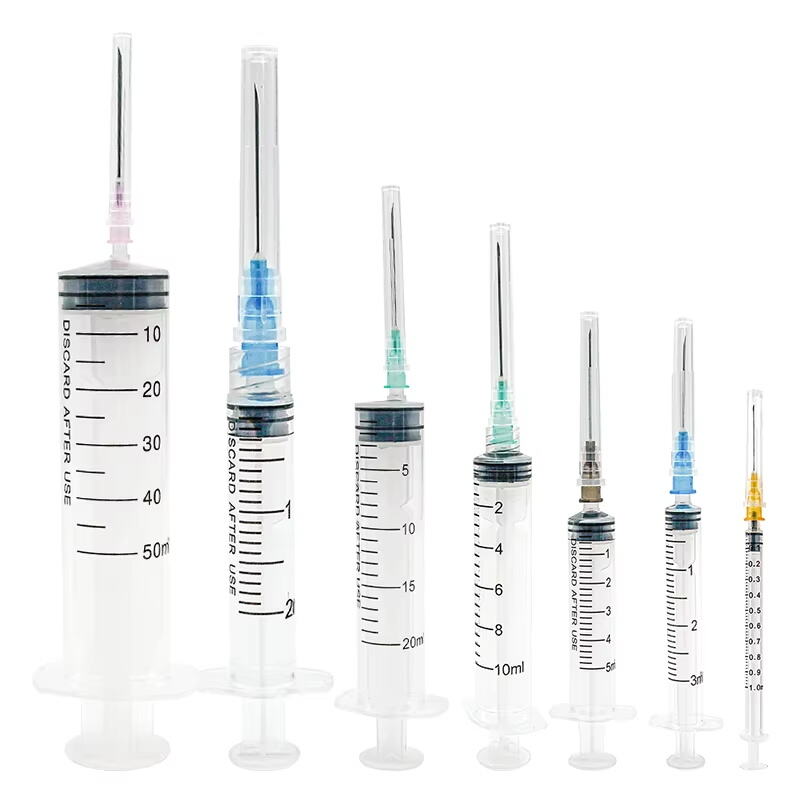
So what actually sets apart those 3ml from 10ml syringes? Knowing how syringes work matters a lot when trying to pick the right one for the job, especially when looking at these two sizes side by side. The 3ml version tends to handle those tiny amounts needed for kids or situations where getting the dose just right is super important. Meanwhile most folks reach for the 10ml option when dealing with bigger shots, which happens quite frequently in regular adult medical treatment or whenever someone needs a substantial amount of meds. These syringes aren't just different in size either. Their barrels vary, plungers come in different lengths too, and even the tips aren't exactly alike across models. All these little details really matter when measuring out medications accurately, something healthcare workers know all too well after years on the job. Getting comfortable with recognizing these differences also means fewer mistakes happen with needles, which makes everyone involved feel safer overall.
Purpose of Needle-Free Designs
Needle free syringes bring real advantages to modern medicine, especially when dealing with large numbers of patients at once. They cut down on those dreaded needle sticks that so many medical staff face daily. For patients who get anxious around needles, this design makes a huge difference in their comfort level during treatment. Another big plus is reduced risk of spreading infections between patients since there's no shared equipment involved. Clinics using these devices report better adherence to vaccine schedules too. When hundreds or even thousands need shots quickly, as happens during outbreaks or routine flu season, needle free systems make the whole process faster and safer. Healthcare providers across various specialties are increasingly adopting these technologies because they simply work better in practice than traditional methods ever did.
Safe Preparation & Handling Procedures
Sterilization Techniques for Reusable Parts
So what counts as good sterilization techniques anyway? Well, most medical facilities rely on methods like autoclaving or ethylene oxide treatments to keep those reusable parts of syringes safe. These processes basically kill off all the germs and bacteria that might otherwise end up inside someone's bloodstream. According to the Centers for Disease Control, following their detailed sterilization guidelines isn't just recommended it's pretty much mandatory if hospitals want to avoid spreading infections between patients. When staff skip steps or rush through the process, bad things happen we've seen entire wards shut down because of contaminated equipment before. That's why ongoing training sessions are so important they help nurses and technicians remember exactly how to handle each piece properly without cutting corners. Better sterilization means fewer hospital acquired infections, which ultimately saves lives and keeps medical costs from spiraling out of control.
Proper Medication Measurement Guidelines
Getting medication measurements right matters a lot. When meds aren't measured properly, patients risk getting too much or too little, which can be dangerous particularly in hospital intensive care units. Nurses and doctors need to pick the right kind of syringe for each situation because different sizes matter when giving out specific doses. Most healthcare workers follow strict protocols about this stuff, checking and rechecking numbers before actually giving someone their medicine. Think about it this way: imagine if a doctor gave half what was needed for an infection treatment just because they grabbed the wrong sized needle by mistake. That's why hospitals have those big posters near medication carts reminding staff to take their time with calculations. Getting these details right helps make sure treatments work as intended while keeping everyone safe throughout the process.
For more information on accurate dosing, you may want to consult the guidelines on syringe measurement safety.
Step-by-Step Injection Best Practices
Skin Preparation & Needle Insertion Angles
When it comes to giving injections, there are several things that really matter. First off, getting the skin ready properly and making sure the needle goes in at the right angle makes all the difference. Cleaning the area with antiseptic before sticking the needle in cuts down on infections quite a bit actually. Studies show that proper cleaning can bring infection rates way down from around 10% to maybe even below 1%. That kind of attention to detail helps get the medicine where it needs to go without causing extra problems later. Needle angles vary depending on what kind of shot we're talking about. For muscle shots, aim straight in at 90 degrees, while fat layer injections need more of a slant at about 45 degrees. Getting this right prevents unnecessary pain and tissue damage. Healthcare workers should refresh their skills regularly on these basics because patients notice when procedures are done well versus rushed through. Good technique leads to better results and happier patients overall.
Preventing Air Bubbles & Tissue Damage
What's the best way to get rid of those pesky air bubbles when giving injections? Getting rid of air bubbles while avoiding tissue damage during injections matters a lot for getting the right dose and keeping patients safe. When there are air bubbles in syringes, sometimes people don't get enough medicine, which makes treatments less effective. That's why nurses and doctors need to know how to push out those bubbles properly. Handling syringes correctly and inserting needles just right helps prevent tissue damage that could cause problems later on like abscesses forming. Healthcare workers should really focus on good techniques for eliminating air bubbles and picking the right spot for injections. With proper training and sticking to what works best, medical staff can avoid unnecessary tissue damage and make sure treatments actually work as intended for their patients.
Disposal Protocols for Used Syringes
Biohazard Container Requirements
Biohazard container requirements matter a lot when it comes to getting rid of used needles safely and keeping everyone from the general public to medical personnel out of harm's way. Containers need to follow strict rules established by OSHA and CDC regulations. They should resist punctures, stay completely sealed against leaks, and stand out visually so people know what they're dealing with. These tough standards exist because we want to make sure no one gets hurt handling or coming across discarded syringes. Regular trash removal schedules along with clear disposal instructions help keep bins from getting too full and stop accidents where someone might touch something dangerous. When hospitals and clinics stick to these safety measures, they create better protection not just for their workers but also for anyone walking through their doors.
Community Syringe Return Programs
What makes community syringe return programs so effective for safety? Well, these programs cut down on the number of used needles lying around in parks, alleys, and other public spaces where people might accidentally step on them. That means fewer needle stick injuries for everyone walking by. Beyond just giving folks somewhere safe to dispose of syringes, many programs actually teach locals about what happens if they throw needles away wrong. Some cities have seen their problems drop dramatically after setting up these collection points. Take Chicago as an example they reported over 50% fewer incidents involving discarded needles once their program got going strong. When regular people know where to take their used equipment, they become part of the solution rather than the problem. Access to proper disposal options really does make neighborhoods safer overall while protecting public health at the same time.
FAQ
Why is syringe reuse dangerous?
Syringe reuse poses significant health risks by potentially transmitting infections like HIV and Hepatitis B/C, and degrading the needle, leading to increased pain and ineffective medication delivery.
How do contaminated syringes spread disease?
Contaminated syringes can spread pathogens and blood-borne diseases rapidly, especially when reused without proper sterilization, leading to high transmission rates.
What are effective sterilization techniques?
Techniques like autoclaving and ethylene oxide treatment are crucial for eliminating pathogens from reusable syringe components, preventing infections.
How is medication measured accurately?
Accurate medication measurement involves using the correct syringe type and size, double-checking doses, following established guidelines to avoid overdose or underdose.
What are biohazard container requirements?
Biohazard containers must be puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and distinguishable to ensure safe disposal of used syringes, complying with OSHA and CDC standards.
How do community syringe return programs enhance safety?
Syringe return programs provide safe disposal resources, reducing public needle-stick injuries and raising awareness on proper disposal protocols, ultimately enhancing community safety.

