Understanding Modern Insulin Administration Tools
Managing diabetes effectively requires precise insulin delivery, making insulin syringes one of the most crucial tools in daily diabetes care. These medical devices have evolved significantly over the years, offering people with diabetes more comfort, accuracy, and convenience in their treatment routines. With various options available today, understanding how to choose and use insulin syringes properly can make a substantial difference in diabetes management.
Essential Components of Insulin Syringes
Barrel Design and Capacity Options
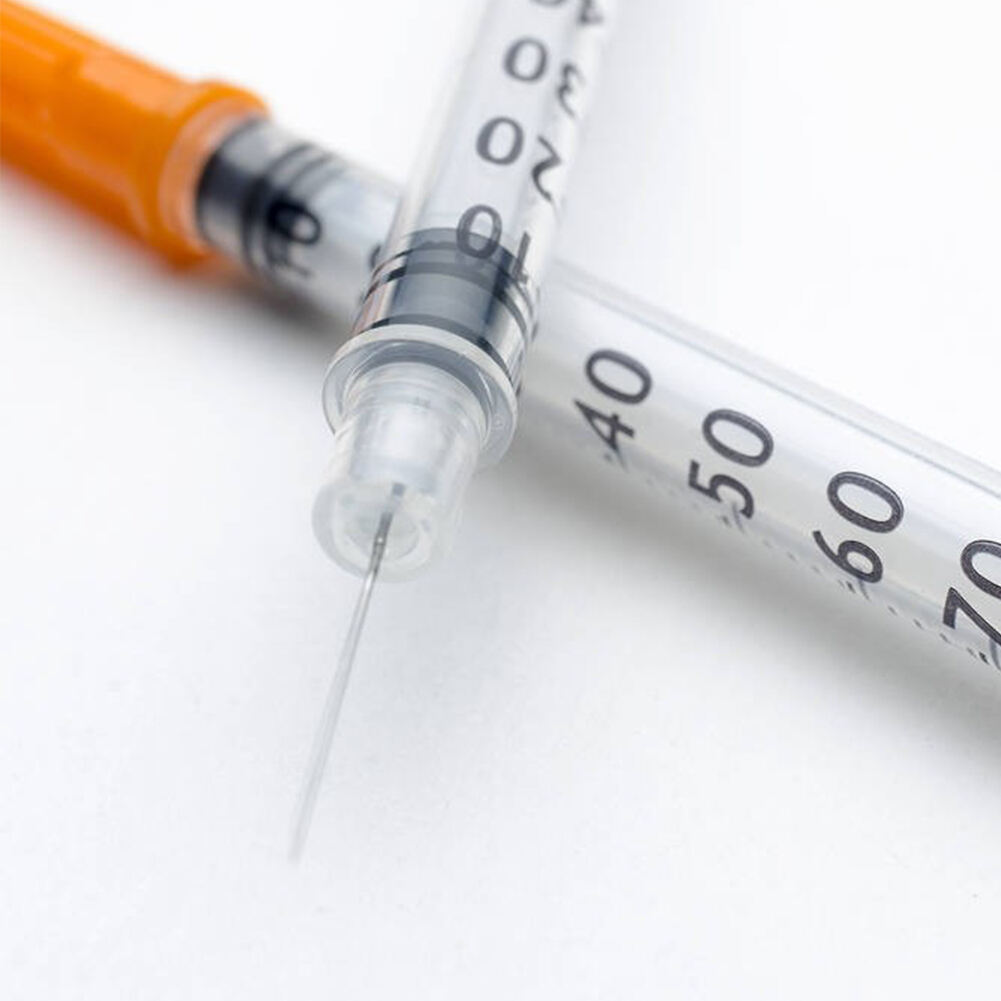
The barrel of insulin syringes comes in different sizes to accommodate various insulin doses. Common capacities include 30-unit, 50-unit, and 100-unit syringes. The barrel features clear, easy-to-read markings that help users measure precise insulin amounts. These markings are specifically calibrated for insulin concentration, typically U-100 in most countries.
Modern insulin syringes incorporate advanced barrel designs that minimize insulin waste and ensure accurate dosing. The interior is coated with special materials that reduce friction and allow smooth plunger movement. This design helps prevent insulin from sticking to the walls, ensuring that patients receive their full prescribed dose.
Needle Technology and Comfort Features
Today's insulin syringes feature ultra-fine needles made from high-grade surgical steel. These needles undergo special treatment processes to ensure maximum sharpness and smooth penetration. The needle length typically ranges from 4mm to 12.7mm, with shorter needles being increasingly popular due to their comfort and effectiveness for most patients.
Advanced coating technologies help reduce injection pain and tissue trauma. Many insulin syringes now feature special lubricating coatings that make insertion smoother and more comfortable. The needle tips are designed with precise angles that minimize tissue damage and reduce the sensation of injection.
Selecting the Right Insulin Syringe
Matching Syringe Size to Dose Requirements
Choosing the appropriate insulin syringe size depends primarily on the prescribed insulin dose. For those requiring smaller doses (30 units or less), a 30-unit syringe offers better precision in measuring. Patients who need larger doses might prefer 50-unit or 100-unit syringes to avoid multiple injections.
The scale markings on insulin syringes become particularly important when precise measurements are needed. Smaller-capacity syringes typically have more detailed marking intervals, making it easier to measure small doses accurately. This precision is especially crucial for children or adults who require minimal insulin amounts.
Needle Length and Gauge Considerations
The selection of needle length depends on various factors, including body type and injection site. Generally, shorter needles (4-6mm) work well for most people and reduce the risk of intramuscular injection. Longer needles might be necessary for some patients, but this should be discussed with healthcare providers.
Needle gauge (thickness) is another crucial factor. Most insulin syringes use gauges between 28 and 31, with higher numbers indicating thinner needles. Thinner needles generally cause less discomfort but may require slightly more time to deliver insulin. The choice often depends on personal preference and the insulin's viscosity.
Proper Storage and Handling Practices
Temperature Control and Storage Conditions
Proper storage of insulin syringes is essential for maintaining their sterility and effectiveness. Unused syringes should be kept in a clean, dry place at room temperature. Avoid storing them in bathrooms or other humid environments that might compromise sterility. It's important to check the packaging for any signs of damage before use.
Temperature fluctuations can affect both the syringes and the insulin they contain. If pre-filled syringes are used, storage requirements become even more critical. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and healthcare provider recommendations regarding storage conditions and duration.
Safe Disposal Methods
Responsible disposal of used insulin syringes is crucial for safety and environmental reasons. Used syringes should always be placed in approved sharps containers, never in regular household trash. Many communities offer specific disposal programs for medical waste, and some pharmacies provide sharps disposal services.
When traveling, portable sharps containers can help maintain proper disposal practices away from home. It's essential to research local regulations regarding medical waste disposal, as requirements can vary by region. Some areas provide free disposal services through healthcare facilities or community programs.
Advanced Tips for Comfortable Injection
Rotation of Injection Sites
Proper rotation of injection sites helps prevent lipohypertrophy (fatty lumps under the skin) and ensures consistent insulin absorption. Create a systematic rotation pattern between different areas such as the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. Within each area, space injections at least one inch apart.
Maintaining a log of injection sites can help track rotation patterns. Some patients find it helpful to divide injection areas into quadrants or sections, moving systematically through each section over time. This organized approach helps prevent overuse of any particular area.
Injection Technique Optimization
Proper injection technique significantly impacts comfort and insulin absorption. Always use a new syringe for each injection, and ensure the injection site is clean. Pinch the skin gently if needed, insert the needle at the correct angle (usually 90 degrees), and inject the insulin slowly and steadily.
Timing matters too - leaving the needle in place for a few seconds after injection helps ensure all insulin is delivered and reduces the chance of leakage. Some patients find that letting insulin reach room temperature before injection increases comfort, though this should be discussed with healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can I reuse insulin syringes?
While insulin syringes are designed for single use, some healthcare providers may approve limited reuse for personal use only. However, this practice isn't officially recommended due to increased risk of infection and needle dulling. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on syringe use.
Can I mix different types of insulin in one syringe?
Some insulin types can be mixed in the same syringe, but this requires careful technique and specific mixing order. Not all insulin types are compatible for mixing. Always follow your healthcare provider's instructions and confirm which combinations are safe for your treatment plan.
What should I do if I see air bubbles in my insulin syringe?
Air bubbles should be removed before injection by gently tapping the syringe barrel and pushing the plunger slightly to expel the air. While small air bubbles aren't dangerous if injected subcutaneously, they can affect dose accuracy. Take time to remove visible air bubbles for precise dosing.
How do I know if I need to change needle length or syringe size?
Consider discussing changes with your healthcare provider if you experience persistent injection discomfort, insulin leakage, or difficulty reading measurement markings. Changes in body weight, injection technique issues, or new insulin prescriptions might necessitate adjusting your syringe specifications.
