Compreendendo Médico Seringa Fundamentos da Seleção
Selecção do direito seringa de injeção é crucial para garantir a administração precisa de medicamentos, o conforto do paciente e resultados terapêuticos ideais. Os profissionais médicos e prestadores de serviços de saúde devem considerar múltiplos fatores ao escolher seringas adequadas para diversas aplicações clínicas. Este guia abrangente explorará os aspectos essenciais da seleção de seringas de injeção, ajudando-o a tomar decisões informadas para sua prática médica ou instalação de saúde.
Componentes Principais das Seringas de Injeção
Design e Materiais do Cilindro
O cilindro da seringa atua como o componente principal que armazena o medicamento e permite a medição precisa. As seringas modernas geralmente são feitas de polipropileno ou policarbonato, oferecendo excelente transparência para leituras precisas da dosagem. O material do cilindro deve ser quimicamente resistente aos medicamentos e manter a integridade estrutural durante o armazenamento e o uso. Seringas de alta qualidade possuem marcações graduadas que permanecem claramente visíveis e não desgastam com o manuseio regular.
Especificações e Compatibilidade da Agulha
A seleção da agulha desempenha um papel fundamental na eficácia da injeção. O calibre (diâmetro) e o comprimento da agulha devem ser adequados ao uso pretendido, ao local da injeção e à viscosidade do medicamento. Números menores de calibre indicam diâmetros maiores da agulha, enquanto números maiores representam agulhas mais finas. Por exemplo, uma agulha de calibre 25 pode ser adequada para injeções subcutâneas, enquanto as injeções intramusculares geralmente exigem agulhas maiores de calibre 21.
Tecnologia do Êmbolo e Vedação
O mecanismo do êmbolo garante operação suave e dosagem precisa. As seringas modernas incorporam vedações especializadas em borracha ou elastômero sintético que mantêm pressão constante e evitam vazamentos de medicamento. O êmbolo deve mover-se suavemente, sem travar ou exigir força excessiva, permitindo aos profissionais de saúde manter controle constante durante os procedimentos de injeção.
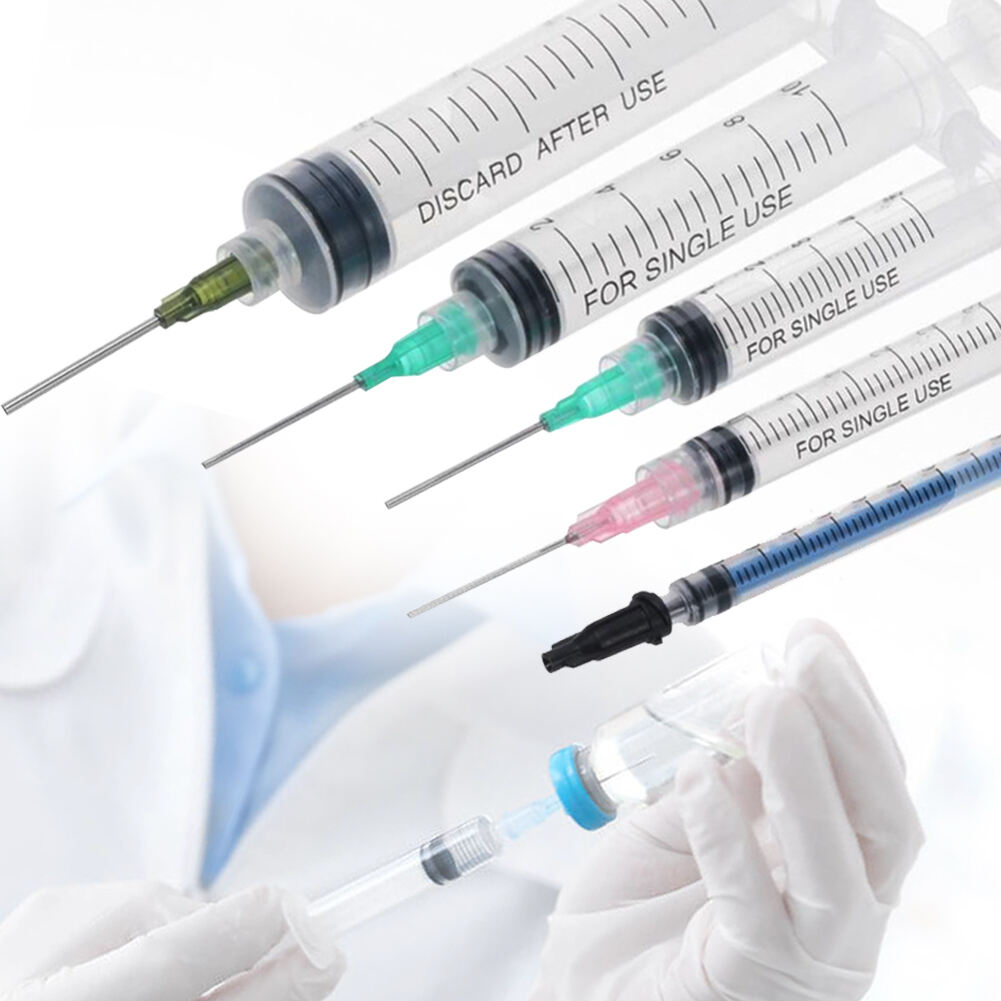
Tipos de Seringas de Injeção para Diferentes Aplicações
Seringas Descartáveis Padrão
As seringas descartáveis normalizadas representam o tipo mais utilizado nos cuidados de saúde. Estas seringas de injecção são de vários tamanhos, normalmente de 1 ml a 60 ml, e apresentam marcas de medição claras. São para uso único para evitar contaminação e garantir esterilidade. A versatilidade das seringas padrão as torna adequadas para múltiplas aplicações, desde simples injeções subcutâneas até procedimentos mais complexos.
Seringas com Engenharia de Segurança
As seringas de segurança incorporam características especiais para evitar ferimentos por agulhas e promover um manuseio mais seguro. Estes podem incluir agulhas retráteis, protetores de agulhas ou outros mecanismos de proteção que se activam após o uso. As instalações de saúde adotam cada vez mais seringas de injeção de engenharia de segurança para cumprir os requisitos regulamentares e proteger os trabalhadores de saúde da exposição acidental a patógenos transmitidos pelo sangue.
Sistemas de injecção especializados
Certos procedimentos médicos exigem projetos especializados de seringas. Por exemplo, as seringas para insulina possuem graduações mais finas para dosagem precisa, enquanto as seringas tuberculínicas oferecem maior precisão para injeções de pequeno volume. Além disso, as seringas pré-cheias eliminam a necessidade de preenchimento manual e reduzem o tempo de preparação do medicamento, sendo particularmente benéficas em situações de emergência ou em ambientes clínicos de alto volume.
Critérios Essenciais de Seleção
Requisitos de Volume
A seleção do tamanho apropriado da seringa depende do volume de medicamento necessário. O uso de uma seringa de injeção muito grande para pequenos volumes pode levar a imprecisões na dosagem, enquanto uma seringa muito pequena pode exigir múltiplas injeções. Os profissionais de saúde devem escolher seringas que permitam que o volume do medicamento caiba dentro da faixa média da capacidade do corpo da seringa para obter a melhor precisão.
Compatibilidade com Medicamentos
Diferentes medicamentos podem exigir materiais específicos de seringas para manter a estabilidade e eficácia. Alguns medicamentos podem interagir com certos plásticos ou componentes de borracha, potencialmente afetando a potência do fármaco ou causando degradação. Sempre verifique a compatibilidade do medicamento com o tipo de seringa escolhido, especialmente para produtos farmacêuticos especializados ou sensíveis.
Considerações sobre a População de Pacientes
A população-alvo de pacientes influencia significativamente a seleção da seringa. Pacientes pediátricos podem necessitar de seringas menores com marcas de graduação mais finas para uma dosagem precisa. Pacientes idosos ou com problemas de destreza podem se beneficiar de seringas com recursos de melhor aderência ou marcações mais fáceis de ler. Considere esses fatores ao definir o estoque de seringas injetáveis da sua instituição.
Garantia da qualidade e conformidade com a regulamentação
Normas de Esterilização
Todas as seringas de injeção devem atender a rigorosos requisitos de esterilização para garantir a segurança do paciente. Procure produtos que estejam em conformidade com as normas internacionais de esterilização e que apresentem indicadores claros de esterilização. A integridade da embalagem deve ser mantida até o momento do uso, com datas de validade e números de lote claramente identificados para rastreabilidade.
Controle de Qualidade na Fabricação
Seringas de alta qualidade passam por processos rigorosos de controle de qualidade durante a fabricação. Isso inclui testes de consistência dos materiais, precisão dimensional e desempenho funcional. Escolha seringas de fabricantes reconhecidos que mantenham sistemas certificados de gestão da qualidade e forneçam documentação detalhada sobre os produtos.
Considerações sobre Custo e Gestão de Suprimentos
Análise de Custo Total
Embora o preço inicial de compra seja importante, considere o custo total de propriedade ao selecionar seringas de injeção. Isso inclui fatores como requisitos de armazenamento, custos com descarte de resíduos e possíveis economias provenientes da compra em grande quantidade. Seringas com sistema de segurança podem ter custos iniciais mais altos, mas podem reduzir despesas relacionadas a acidentes com agulhas e aos tratamentos associados.
Estratégias de Gestão de Inventário
Um gerenciamento eficiente de estoque garante disponibilidade constante, minimizando ao mesmo tempo o desperdício. Implemente sistemas de rotação de estoque para evitar a expiração de seringas armazenadas e considere sistemas automatizados de rastreamento de inventário para instalações maiores. A avaliação regular dos padrões de uso ajuda a otimizar as quantidades pedidas e a utilização do espaço de armazenamento.
Perguntas Frequentes
Quais fatores determinam a bitola adequada da agulha para uma injeção?
A espessura apropriada da agulha depende de vários fatores, incluindo a viscosidade do medicamento, o local da injeção, a profundidade necessária de penetração e o conforto do paciente. Injeções subcutâneas normalmente utilizam agulhas de 25 a 30 gauge, enquanto injeções intramusculares podem exigir agulhas de 18 a 23 gauge para uma administração adequada.
Por quanto tempo seringas estéreis não utilizadas podem ser armazenadas?
As seringas estéreis para injeção têm normalmente um prazo de validade de 3 a 5 anos quando armazenadas corretamente na embalagem original. No entanto, isso pode variar conforme o fabricante e as condições de armazenamento. Sempre verifique a data de validade e certifique-se de que os locais de armazenamento mantenham níveis apropriados de temperatura e umidade.
Existem seringas específicas obrigatórias para determinados medicamentos?
Sim, alguns medicamentos requerem tipos específicos de seringas de injeção devido a problemas de compatibilidade ou requisitos de dosagem. Por exemplo, a insulina exige seringas especializadas com marcações precisas, enquanto alguns biológicos podem necessitar de composições materiais específicas para manter a estabilidade do medicamento. Consulte sempre as orientações do medicamento e as recomendações do fabricante para a seleção adequada da seringa.
Como as instalações de saúde podem garantir a correta descarte das seringas usadas?
As instalações de saúde devem seguir as regulamentações locais e os protocolos estabelecidos para o descarte adequado de seringas de injeção usadas. Isso geralmente inclui o uso de recipientes aprovados para objetos perfurocortantes, a implementação de procedimentos claros de segregação e a parceria com serviços certificados de descarte de resíduos médicos. A capacitação regular da equipe sobre os métodos corretos de descarte é essencial para manter a segurança e a conformidade.
Sumário
- Compreendendo Médico Seringa Fundamentos da Seleção
- Componentes Principais das Seringas de Injeção
- Tipos de Seringas de Injeção para Diferentes Aplicações
- Critérios Essenciais de Seleção
- Garantia da qualidade e conformidade com a regulamentação
- Considerações sobre Custo e Gestão de Suprimentos
-
Perguntas Frequentes
- Quais fatores determinam a bitola adequada da agulha para uma injeção?
- Por quanto tempo seringas estéreis não utilizadas podem ser armazenadas?
- Existem seringas específicas obrigatórias para determinados medicamentos?
- Como as instalações de saúde podem garantir a correta descarte das seringas usadas?