The Evolution of Modern Medical Injection Devices
The healthcare landscape has been revolutionized by the continuous advancement of medical devices, with injection syringes standing as a cornerstone of modern medicine. These essential tools have transformed from simple glass tubes to sophisticated medical instruments that ensure precise medication delivery and patient safety. Today's healthcare professionals rely on injection syringes for everything from routine vaccinations to complex therapeutic treatments.
The impact of injection syringes extends far beyond hospital walls, playing a vital role in home healthcare, clinical research, and public health initiatives. As medical technology continues to evolve, these instruments have adapted to meet increasingly stringent safety standards and diverse medical needs. Understanding their significance in daily healthcare can help both medical professionals and patients appreciate the complexity and importance of these seemingly simple devices.
Components and Design Features of Modern Syringes
Essential Parts and Materials
Modern injection syringes comprise several carefully engineered components, each serving a specific purpose. The barrel, typically made from medical-grade plastic, provides a transparent chamber for measuring and containing medication. The plunger, equipped with a rubber stopper, ensures smooth movement and proper seal formation. The needle hub and shaft are designed for optimal penetration while minimizing patient discomfort.
Advanced materials used in contemporary injection syringes include polypropylene for the barrel, silicone-coated rubber for the plunger, and surgical-grade stainless steel for needles. These materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure biocompatibility and durability, making modern syringes both safe and reliable for medical use.
Safety Mechanisms and Innovations
Recent innovations in syringe design have prioritized safety features to protect both healthcare workers and patients. Retractable needle systems automatically withdraw the needle into the barrel after use, preventing accidental needle sticks. Safety shields and needle covers provide additional protection during disposal, while clear markings and color coding help prevent medication errors.
Smart syringes with auto-disable features have emerged as a solution to prevent reuse in clinical settings. These technological advances demonstrate the industry's commitment to enhancing safety standards while maintaining the efficiency of injection syringes in daily healthcare procedures.
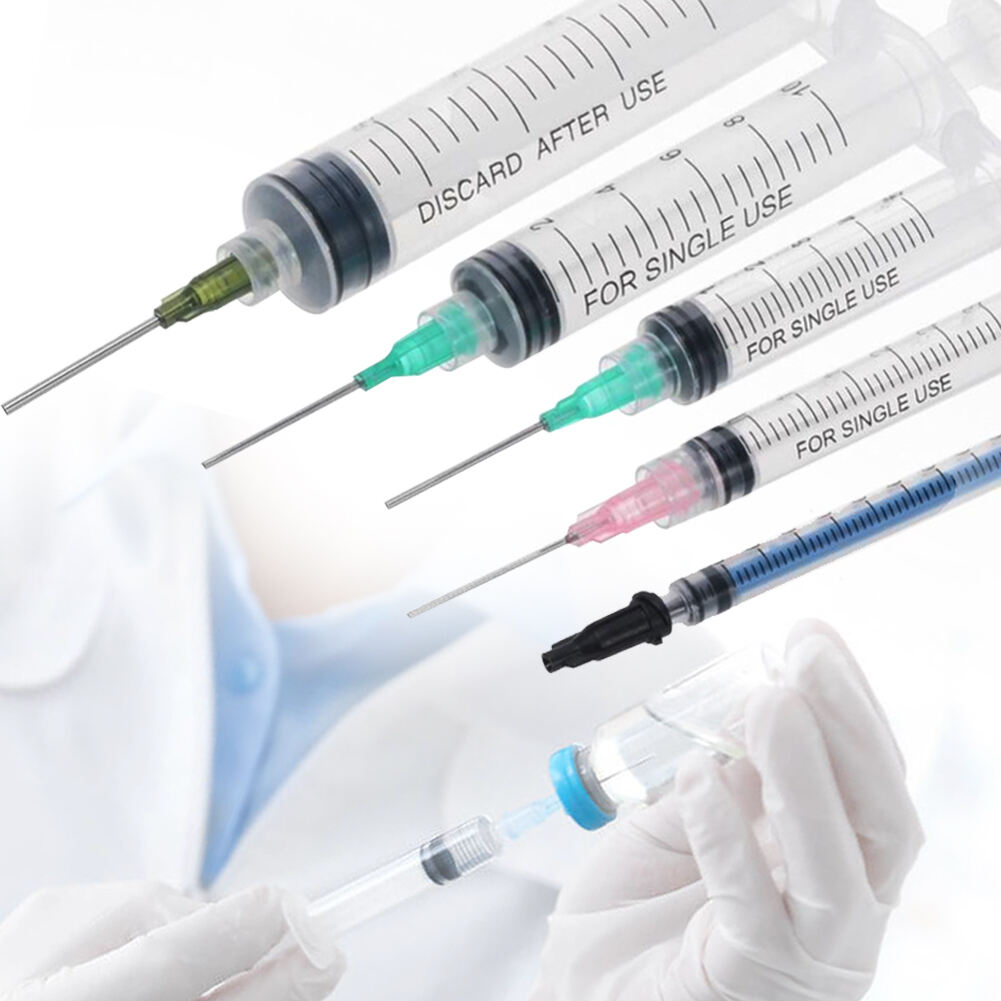
Applications in Various Healthcare Settings
Clinical and Hospital Usage
In clinical environments, injection syringes serve multiple purposes, from administering medications and vaccines to collecting blood samples. Healthcare professionals rely on different syringe sizes and types depending on the specific procedure, medication volume, and patient requirements. The precision of modern injection syringes allows for accurate dosing, which is crucial in treatments requiring exact measurements.
Specialized units like intensive care and emergency departments often use injection syringes with advanced features such as prefilled medications or connection systems compatible with IV lines. These adaptations help streamline care delivery and reduce the risk of medication errors in high-stress situations.
Home Healthcare Applications
The rise of home healthcare has increased the importance of user-friendly injection syringes for patients managing chronic conditions. Diabetic patients, for instance, depend on insulin syringes or pen devices for daily medication administration. These devices are designed with features that make self-injection safer and more comfortable, including improved grip surfaces and clearer measurement markings.
Home care providers and patients receive training on proper injection techniques and syringe disposal, ensuring safe and effective medication delivery outside clinical settings. The availability of specialized injection syringes for home use has significantly improved patient independence and treatment compliance.
Quality Control and Regulatory Standards
Manufacturing Guidelines
The production of injection syringes follows strict quality control measures and international standards. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, ensuring consistent product quality and safety. Each batch undergoes rigorous testing for sterility, material integrity, and functionality before distribution to healthcare facilities.
Regular audits and quality assessments help maintain high manufacturing standards, while continuous monitoring systems track product performance and identify potential improvements. These measures ensure that injection syringes meet the demanding requirements of modern healthcare delivery.
Sterilization and Packaging
Proper sterilization and packaging are crucial aspects of injection syringe production. Advanced sterilization methods, including gamma radiation and ethylene oxide treatment, eliminate potential contaminants while preserving product integrity. Specialized packaging materials and designs maintain sterility until the point of use, with clear indicators showing sterilization status.
Environmental considerations have led to innovations in packaging materials and designs that reduce waste while maintaining product safety. These developments reflect the industry's commitment to sustainability without compromising the essential sterility of injection syringes.
Future Trends and Innovations
Smart Technology Integration
The future of injection syringes lies in smart technology integration. Connected devices capable of tracking injection times, doses, and patient compliance are already in development. These smart syringes can potentially communicate with healthcare providers through mobile applications, improving treatment monitoring and patient care coordination.
Emerging technologies also include needle-free injection systems and microneedle arrays, which could revolutionize how medications are delivered. These innovations aim to enhance patient comfort while maintaining the accuracy and reliability that traditional injection syringes provide.
Sustainable Development
Environmental consciousness is driving the development of more sustainable injection syringe solutions. Biodegradable materials and recycling programs for medical waste are becoming increasingly important. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly production methods and materials that maintain medical standards while reducing environmental impact.
Research into reusable components and alternative materials continues, with the goal of creating more sustainable healthcare practices without compromising safety or effectiveness. These developments represent a significant step toward more environmentally responsible medical device production.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can injection syringes be safely stored?
Sterile injection syringes typically have a shelf life of 3-5 years when stored properly in their original packaging at room temperature. However, it's essential to check the expiration date and ensure the packaging remains intact before use.
What are the different types of injection syringes available?
Common types include conventional syringes, safety syringes with needle protection mechanisms, insulin syringes, tuberculin syringes, and prefilled syringes. Each type is designed for specific medical applications and may have different features and capacities.
How should used injection syringes be disposed of safely?
Used injection syringes must be disposed of in approved sharps containers to prevent needle stick injuries and contamination. These containers should be sealed when full and disposed of according to local medical waste regulations, either through healthcare facilities or authorized disposal services.